Computed Radiography [CR]
Digital or Computed radiography [CR] is the digital replacement of conventional X-ray film radiography and offers enormous advantages for inspection tasks. The use of consumables is virtually eliminated and the time to produce an image is drastically shortened.
Instead of film, an imaging plate is exposed to X-ray or gamma radiation. The imaging plate is digitised by the scanner and then erased for immediate reuse. The digital image is then displayed on a computer monitor for evaluation with specialised software.
The most important benefit is that CR is a Non-Intrusive inspection, meaning it is performed while the asset is in service.
As with every digital transition the improvement lies in efficiency & accuracy:
- Imaging plates are reusable
- No darkroom or chemicals needed
- Reduction in exposure and processing time
- Software-based evaluation and reporting provide higher sizing accuracy
- Simple digital data exchange and archiving
Furthermore, more details are visible and analysable with computed radiography due to a higher dynamic range when compared to film. Other advantages over film include a more simplified workflow, a safer working environment for operators and a more environmentally-friendly chemical-free process.
Here’s what you should consider before the application of CR testing:
- Radiation safety considerations are the same for CR as standard radiography.
- Requires access to both sides of the part under examination.
- An additional equipment reading station is required to scan the imaging plates.
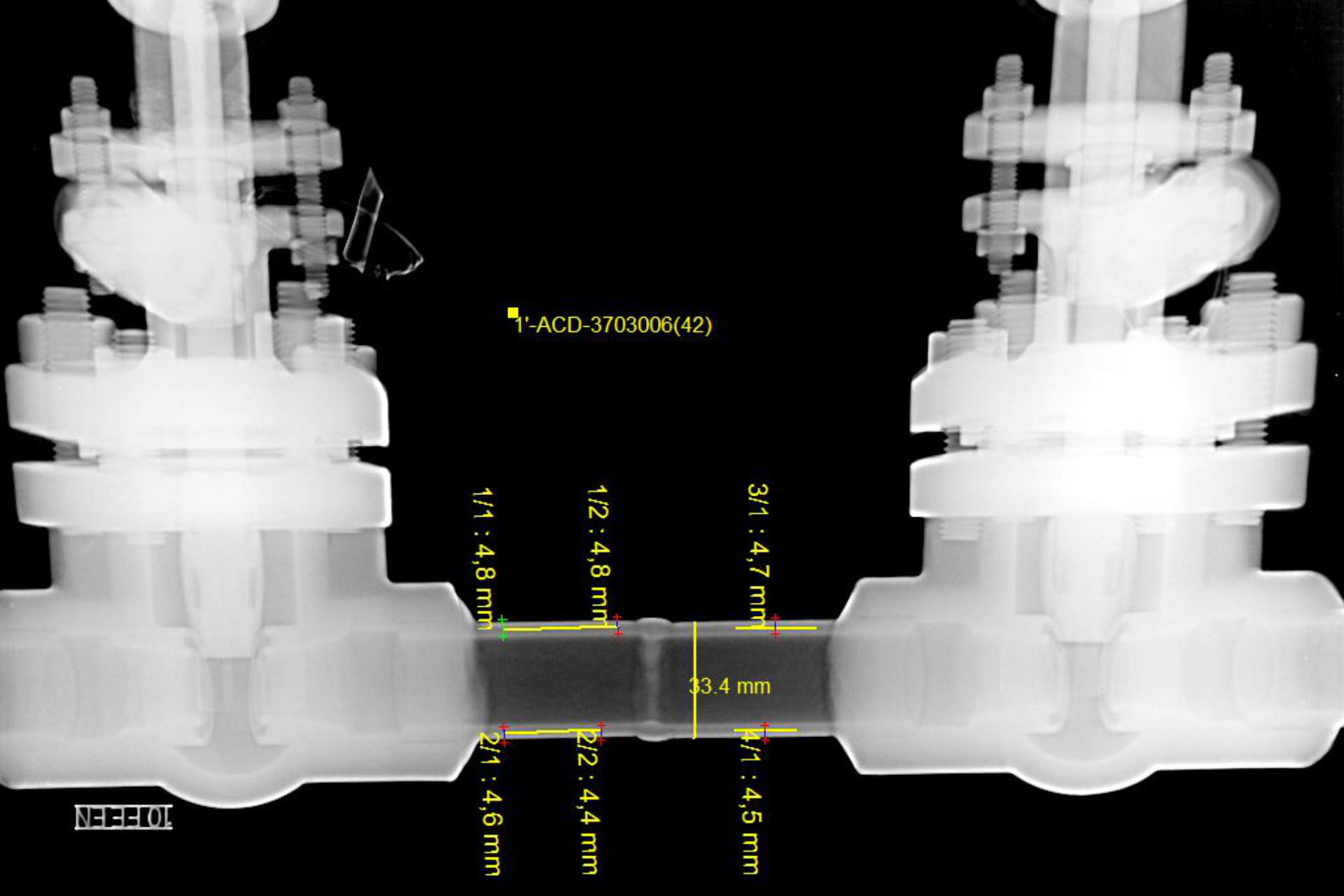
Computed Radiography inspection is vital in fields such as oil and gas and electronics where the integrity of materials is vital for safety and cost reasons. On-stream inspection for composite materials, pipes leakage, weld wall thickness to determine corrosion, and castings are among the most common applications for CR.
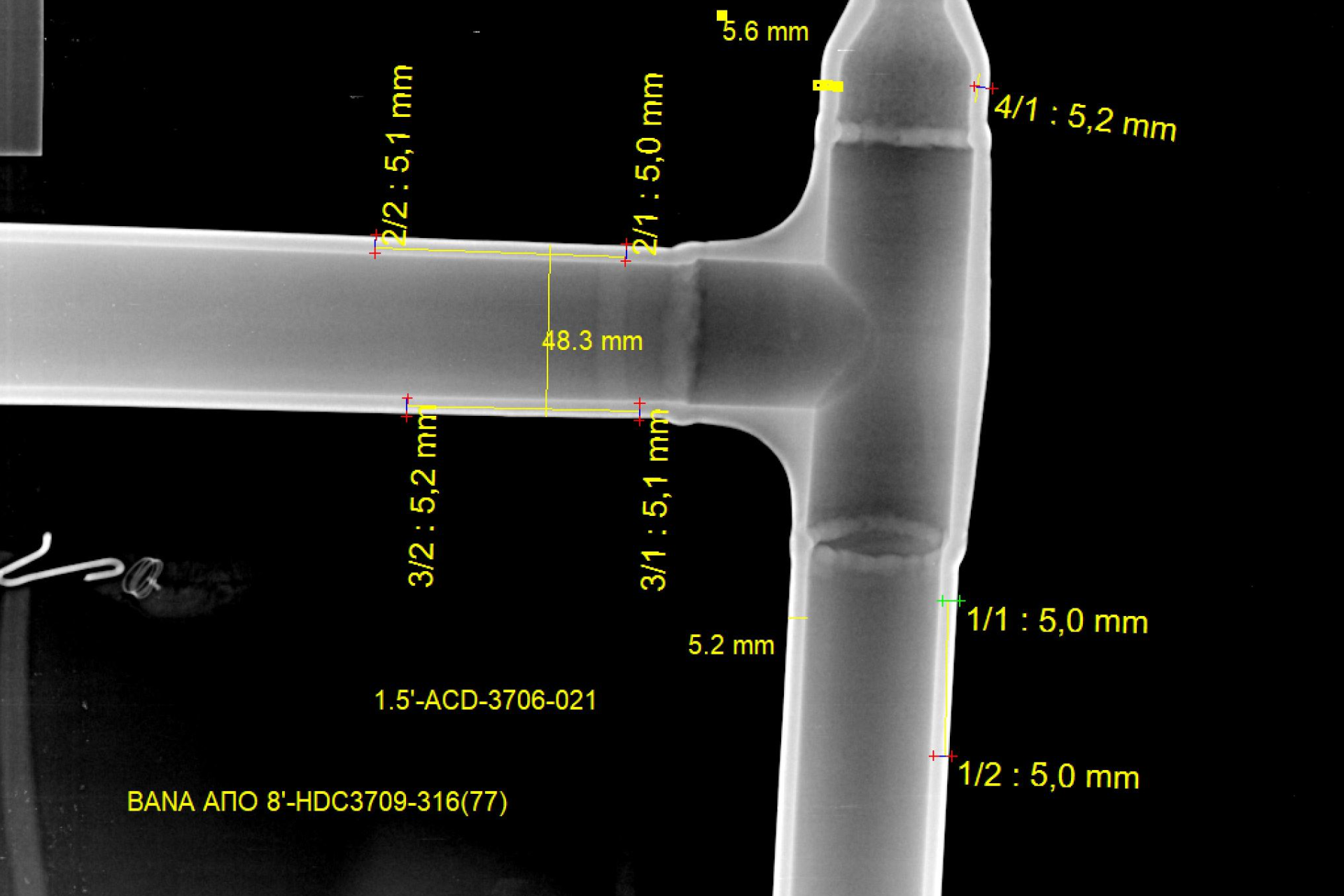
Newtron Computed Radiography services can be used to assess a wide array of assets in:
- Static & pressurised equipment
- Pipelines
- Tanks
- Composite materials
International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
ISO 20769-2 Non-destructive testing — Radiographic inspection of corrosion and deposits in pipes by x- and gamma rays — Part 2: double wall Radiographic inspection (2018)
ISO 20769-1 Non-destructive testing — Radiographic inspection of corrosion and deposits in pipes by x- and gamma rays — Part 1: tangential Radiographic inspection (2018)
ISO 17636-2 Non-destructive testing of welds — Radiographic testing — Part 2: x- and gamma-ray techniques with digital detectors (2013)
ISO 10893-7 Non-destructive testing of steel tubes — Part 7: digital Radiographic testing of the weld seam of welded steel tubes for the detection of imperfections (2019)
ISO 16371-2 Non-destructive testing — industrial computed Radiography with storage phosphor imaging plates — Part 2: general principles for testing of metallic materials using x-rays and gamma rays (2017)
European Committee for Standardization (CEN)
EN 14096 Non-destructive testing – Qualification of radiographic film digitisation systems
EN 14784-1 Non-destructive testing – Industrial computed radiography with storage phosphor imaging plates – Part 1: Classification of systems
EN 14584-2 Non-destructive testing – Industrial computed radiography with storage phosphor imaging plates – Part 2: General principles for testing of metallic materials using X-rays and gamma rays
American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME)
ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section V
This information is a collection of references. While we have made every attempt to ensure that information on this site is updated, Newtron is not responsible for any errors or omissions, or for the results obtained from the use of this information. It is not guaranteed to be complete, correct, current, or up to date and may be changed without prior notice.
